Perspectives
Beating the Odds: How Digital Health is Advancing Cancer Diagnosis, Care, and Survivorship

A new cancer diagnosis is delivered every 30 seconds in the United States, with rates showing no signs of slowing.[1],[2] Current projections indicate that the number of cancer cases will grow by 35% over the next ten years.[3] This merciless disease has claimed the lives of many and will continue to do so, leaving a trail of loss for families, friends, and caregivers in its wake.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic is expected to contribute to an increase in cancer case severity in the near term. Cancer diagnostic procedures and treatments have been delayed or de-prioritized by health systems due to newly enacted CDC recommendations. As a result, survival rates are projected to decrease by 5-10%.[4] It is clear that the rapid advancement of innovative treatments and diagnostics for early detection are more important than ever before.
The multi-faceted nature of cancer and the multitude of factors that impact each individual consumer’s risk level and disease progression adds to the challenge of rapidly diagnosing, appropriately treating, and effectively managing the disease. Cancer is not just genetic; in fact, mutations caused by environmental and lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, chemicals, viruses, and hormones play a role in 90-95% of cancer cases.[5],[6] Cancer care, therefore, requires highly personalized disease management, with treatment plans that account for an individual’s comorbidities, social factors, and genetic profile.
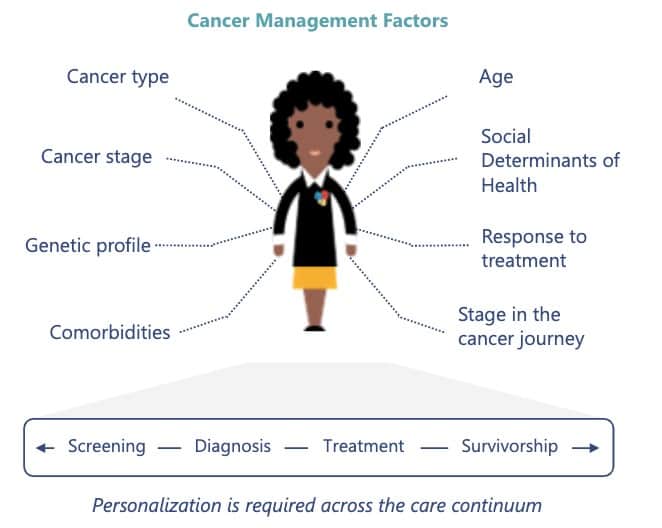
With that said, meaningful progress has been made in cancer care over the last century. New therapies, an improved understanding of causes, targeted treatments, genomics, and personalized medicine have all served to drive earlier diagnoses and improve outcomes. In fact, the five-year survival rate has increased over 20 percent in the last three decades.[7]
Despite these advances, major obstacles still exist in navigating the cancer care journey due to complicated care coordination, rising treatment costs, low clinical trial participation, provider administrative burden, emotional hardship for patients and their caregivers, and long development pathways for new treatments.
Oncology Digital Health Solutions
Technology is transforming every stage of the cancer journey, creating opportunities to fundamentally improve care and address existing barriers. These advances enable care that is increasingly personalized – tailored to the individual demographic, clinical, and genetic profile and unique needs of each cancer patient.
Digital health solutions in oncology have benefited from increased investment over the last several years, led by companies focused on diagnostics and detection, research and data management, and clinical decision support. With new technologies rapidly entering the oncology space, deal count has followed and steadily increased.[8]
At 7wireVentures, we view investments in the oncology digital health market in five distinct categories: Care Navigation and Patient Support, Clinical Trial Optimization, Detection and Diagnostics, Research and Data Management, and Clinical Decision Support. Innovations in these five major categories are changing the way cancer care is advanced, accessed, and delivered.
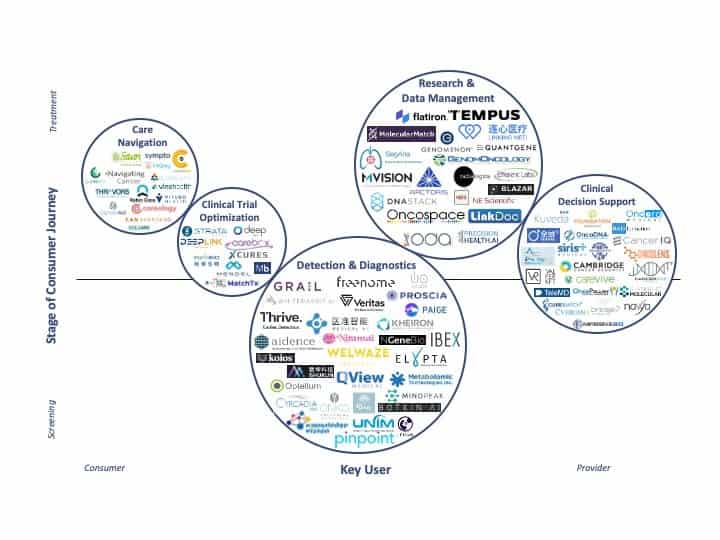
Care Navigation & Patient Support: The use of patient-reported outcomes has surged in oncology due to encouraging clinical results; studies have shown that patients who report their symptoms via online tracking programs live an average of five to seven months longer than those who do not.[9] Adoption of these programs, in combination with the increasing presence of tele-health and connected devices, has driven the development of new solutions for patient support and remote data collection. Companies in this segment are developing tools and platforms to help cancer patients and their care teams to better navigate the care journey and holistically manage their health and symptoms.
Clinical Trial Optimization: Today, less than 5% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. Clinical trial enrollment for cancer therapy is critical, as enrolling patients at a higher rate enables faster treatment development and improved outcomes.[10] Companies in this sector are developing digital offerings to improve clinical development processes, including trial matching, recruitment, screening, consent, monitoring, execution, and follow-up.
Detection & Diagnostics: Technological advances have enabled more timely and comprehensive oncology diagnostics. For example, AI-assisted imaging has been shown to improve the detection of cancer by 13% and reduce the need for excessive biopsies.[11] Next-Gen Sequencing (NGS) can also be used to identify individuals at higher risk of developing cancer and to make more specific and complete diagnoses.[12] Emerging companies in this space are creating digital tools and software designed to aid the detection and diagnosis of various cancer types.
Research & Data Management: An estimated 80% of oncology EHR data is captured and stored in an unstructured format, resulting in limited usability for studying treatment efficacy and safety.[13] Collaborative efforts have focused on developing new data standards to enable the use of massive amounts of data in algorithm-driven tools. Providers and life sciences companies are also incorporating the use of Real-World Evidence (RWE) to address safety and efficacy questions. Solutions in this sector are aimed at advancing the collection, organization, interpretation, and sharing of data.
Clinical Decision Support: Data sharing and machine learning have enabled improved collaboration and decision-making in oncology. The use of AI also has the potential to alter treatment choices, with one study finding that a physician panel changed its treatment decisions in 13% of cases when presented with AI-derived treatment options.[14] Such solutions are used by clinicians, care teams, and patients to improve decision-making once an initial diagnosis has been made.
7wireVentures Predictions
PREDICTION 1: Accelerated adoption of advanced trial matching and remote trial execution, will break down long-standing barriers that have complicated patient access to therapeutic advances.
Point-of-diagnosis clinical trial matching will further accelerate and expand access to the most promising therapies for consumers. Digital tools will reduce the burden of conducting multi-site, in-person clinical trials and increase participation by pre-screening qualified individuals. Such tools will make way for at-home trial participation with the aid of remote monitoring, tele-health, and connected devices. Enhanced collection of longitudinal data through digital platforms will optimize decision making, support development of synthetic control arms, and provide critical outcomes data. The new ecosystem of digitized, connected clinical trial execution will ultimately result in expanded access for consumers, expedited development for pharma, and ultimately drive down treatment costs for all healthcare stakeholders.
PREDICTION 2: Payers will expand coverage for novel diagnostic and management tools, enhancing patient adoption and driving successful management for a variety of cancer types.
As long-term cancer care starts to mirror the management of other chronic diseases, digital tools will become increasingly important in improving medication adherence, preventing complications, and delivering care. Digital tools in the form of automated risk assessments and predictive models will help clinicians make appropriate recommendations and triage patients to the right follow-up services, reducing costs for payers in the long-term. Patient support tools will help structure care coordination, allowing for early intervention and holistic treatment. Companies in this space that can prove a clear business case by improving health outcomes and reducing costs will be the most likely to obtain coverage from payers.
PREDICTION 3: In order to manage increasingly complex treatment plans and make timely clinical decisions, providers will leverage digital tools that streamline data aggregation and provide access to expert clinical guidance.
As treatment options and regimens become more sophisticated, front-line providers will rely on real-time access to clinical pathways and guidance developed by leading institutions. Digital platforms will help oncologists and their care teams stay abreast of the latest clinical trials and therapeutic options. Cloud technologies, combined with increased adoption of universal standards, will support improved data sharing and aggregation across different sources and institutions. Longer term, access to expert-driven clinical pathways will become democratized for providers and be consistently updated based on newly developed protocols.
PREDICTION 4: The COVID-19 pandemic will heighten pressure on healthcare organizations to adopt remote capabilities needed to accelerate therapeutic development and provide adequate care for individuals at risk of or living with cancer.
Patients undergoing many forms of cancer treatment face increased susceptibility to the COVID-19 virus, creating an indefinite need for alternative care options that limit in-person contact. Survivors who routinely receive ongoing care and follow-up exams in-person will be forced to adopt tele-health solutions in the short-term and may in the long-term leverage alternative at-home scanning and monitoring tools to detect abnormalities such as the presence and growth of tumors.
The advancement of technology, coupled with vast unmet needs across the cancer care journey has resulted in the entry and acceleration of many digital health startups in the oncology care market, fueled by increasing support from venture capital. The companies that are primed to succeed are those focused on all stakeholders involved in the cancer care, including researchers, providers, payers, and above all, consumers. As digital health increasingly enables consumers to access to more affordable, personalized, and higher quality cancer treatments, there is great promise of evolving to a holistic and highly effective model of tackling cancer.
[8] Pitchbook